Single vs Dual Socket Dedicated Servers: Which Offers Better Performance?
Single socket server or dual socket server decisions usually surface when performance stops behaving predictably. Applications scale unevenly, latency fluctuates under load, or infrastructure costs rise without a clear improvement in throughput. At this stage, teams are no longer comparing basic specifications. They are trying to understand how CPU architecture affects real workloads, long term efficiency, and operational stability.
This article provides an in depth, practical comparison of single vs dual socket dedicated server architectures, focusing on performance behaviour, cost structure, and workload alignment rather than theoretical maximums.
Understanding Modern Single Socket Server Architecture
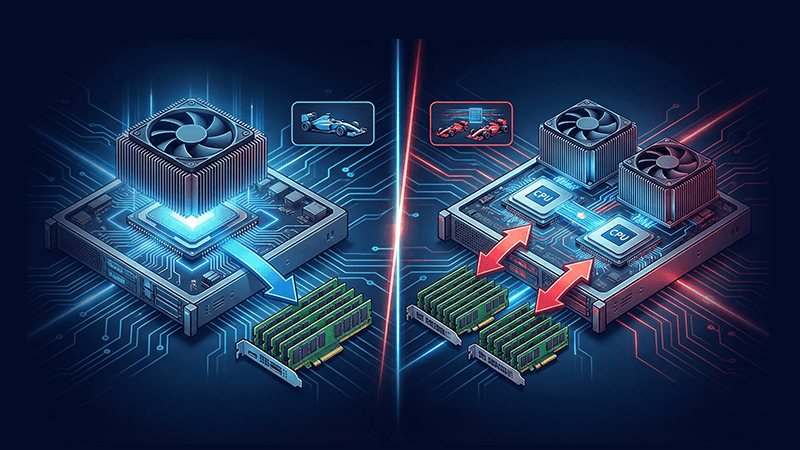
A single socket server today is very different from what it was a decade ago. Modern data center CPUs integrate extremely high core counts, wide memory bandwidth, large shared caches, and extensive PCIe connectivity into a single processor. This means one socket can now handle workloads that previously required two.
From an architectural perspective, a single socket dedicated server operates within a unified compute and memory domain. All CPU cores access memory with uniform latency. There is no cross socket communication and no distinction between local and remote memory. This uniformity reduces variability and makes performance easier to predict, especially under mixed or bursty workloads.
For many real world applications, this consistency is more valuable than adding raw core count.
How Dual Socket Servers Are Designed
A dual socket server installs two physical CPUs on the same motherboard. Each CPU has its own memory channels and PCIe lanes. The processors communicate through interconnects such as Intel UPI or AMD Infinity Fabric.
This design increases total core and memory capacity, but it introduces Non Uniform Memory Access. Memory attached to one CPU is accessed faster than memory attached to the other. If applications are not explicitly NUMA aware, threads can frequently access remote memory, increasing latency and reducing effective throughput.
Dual socket servers are powerful, but they demand more from the software stack and system tuning to deliver consistent performance.
Single Socket vs Dual Socket CPU Performance in Real Workloads
In a dedicated server performance comparison, CPU architecture often matters more than headline specifications.
Single socket servers typically provide:
- Consistent memory latency across all cores
- Predictable cache behaviour
- Simpler CPU scheduling
- Lower inter core communication overhead
Dual socket servers typically provide:
- Higher aggregate core density
- Larger total memory capacity
- Better consolidation for highly parallel workloads
In practice, many production workloads do not scale cleanly across sockets. Web servers, APIs, databases, and transactional systems often benefit more from fast, uniform memory access than from additional cores spread across two CPUs.
This is why modern single socket servers frequently outperform dual socket servers in latency sensitive or moderately parallel environments.
NUMA Effects and Performance Variability
NUMA behaviour is one of the most common hidden issues in dual socket systems. When a process running on one CPU accesses memory attached to the other CPU, latency increases. This affects databases, in memory caches, JVM based services, and containerised applications that were not designed with NUMA awareness.
Operating systems attempt to manage this with NUMA balancing, but it is not perfect. Thread migration, memory fragmentation, and uneven load distribution can introduce performance jitter that appears as inconsistent response times.
Single socket servers avoid NUMA complexity entirely, which is a major reason they are increasingly preferred for production workloads that demand stability.
Dedicated Server Performance Comparison Beyond Benchmarks
Synthetic benchmarks often show dual socket servers achieving higher multi threaded scores. Real applications behave differently.
Production environments include:
- Mixed read and write patterns
- Bursty traffic rather than steady load
- Cache misses and garbage collection
- Network interrupts and I O contention
Under these conditions, the architectural simplicity of a single socket server often results in better sustained performance and fewer tuning requirements. Fewer moving parts mean fewer unpredictable bottlenecks.
Many infrastructure teams report that replacing older dual socket systems with modern high core single socket servers improves real world performance while reducing power and cooling demands.
Cost, Power, and Licensing Considerations
Dual socket servers consume more power and generate more heat. Over time, this increases cooling and energy costs. In dense data center environments, power efficiency directly affects scalability.
Software licensing can further influence the decision. Some enterprise software is still licensed per socket. In these cases, moving to a single socket server with more cores can significantly reduce licensing costs without sacrificing performance.
From a total cost of ownership perspective, single socket servers often deliver better efficiency for common business workloads.
When Dual Socket Servers Still Make Sense
Dual socket servers remain the right choice for certain scenarios:
- Heavy virtualisation with many guests
- High performance computing and scientific workloads
- Large scale parallel data processing
- Applications requiring extremely high memory capacity
When workloads are designed to respect memory locality and thread placement, dual socket systems can deliver exceptional density and throughput.
When Single Socket Dedicated Servers Are the Better Fit
Single socket dedicated servers are particularly well suited for:
- Web hosting and ecommerce platforms
- SaaS applications and APIs
- Relational and NoSQL databases
- Financial and transactional systems
- Content delivery and media services
These workloads benefit from predictable latency, simpler tuning, and lower operational complexity.
Single vs Dual Socket Dedicated Server Strategy Today
As CPU capabilities continue to increase, the industry is steadily moving toward fewer sockets per server. Many modern infrastructures scale horizontally with single socket servers rather than vertically with dual socket machines.
This approach improves fault isolation, simplifies capacity planning, and aligns well with modern application architectures and DevOps practices.
Dataplugs Dedicated Servers and CPU Architecture Flexibility
Choosing between a single socket server and a dual socket server should be based on how applications behave in production, not on assumptions or outdated models.
Dataplugs dedicated servers offer flexible configurations across single socket and dual socket architectures, allowing businesses to align hardware design with real workload requirements. With enterprise grade infrastructure, stable high bandwidth connectivity, and full control over system configuration, Dataplugs provides a reliable foundation for performance driven deployments.
Whether the priority is low latency consistency, high core density, or long term cost efficiency, Dataplugs dedicated server solutions support informed infrastructure decisions without unnecessary complexity.
Conclusion
The question of single vs dual socket dedicated server performance is no longer about which option is universally better. It is about matching CPU architecture to workload behaviour, performance expectations, and operational goals.
Modern single socket servers deliver outstanding performance for a wide range of applications, often matching or exceeding dual socket systems in real world conditions. Dual socket servers continue to play an important role where workloads can fully exploit their architecture.
Understanding these trade offs allows organisations to build infrastructure that scales efficiently and predictably.
To explore dedicated server solutions tailored for modern workloads and performance sensitive environments, connect with Dataplugs via live chat or email at sales@dataplugs.com.